Epidemics are one of the many problems plaguing the world and mankind. The people of the world look at these epidemics with fear. Animal-borne diseases are increasing day by day. Are animal-borne diseases a threat to mankind? Diseases that are transmitted from animals to humans are called zoonotic diseases. Diseases that are transmitted from humans to animals are called anthroponosis. Sixty percent of infectious diseases are said to be zoonotic. Similarly, seventy-five percent of new generation diseases are animal-borne. We need to be extra careful because we can get animal diseases through viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Air, water, contact, food, animal bites, etc., can cause the disease and spread in the same way. Some of the zoonotic diseases causing fear at the global level are Anthrax, Salmonellosis, MERS coronavirus, Nipa, Tuberculosis, Zika, Rabies, Ebola, Avian influenza, and Disease X. Along with understanding why animal-borne diseases have come out of the wild and into the country, we can also learn about some of the animal-borne diseases.
Anthrax- an animal-borne disease that affects animals
Animal-borne diseases from the wild to humans are not a new story. Anthrax is a zoonotic disease that affects all animals, from elephants to humans, but is most devastating to cattle and goats. Bacillus anthracis, which forms spores, causes anthrax, a serious illness. The disease primarily affects animals. By inhaling spores or contacting an infected animal, humans can become infected. In most parts of the world, the anthrax bacteria found naturally in the soil can transmit the disease to cattle, horses, wild boars, and deer under favorable conditions. Humans become infected through contact with infected animals or their meat or skin. Germs usually enter the body through a wound. Infection can occur by eating or inhaling contaminated meat. If the germs from infected animals enter the atmosphere, they form a sheath around them and transform into spores. These spores do not die in any adverse environment. It can be transmitted to animals by eating the flesh of infected individuals or by inhalation. There are four types of anthrax infection, each with different symptoms.
Cutaneous Anthrax
Infection can occur on the skin through cuts or other sores. It is not serious and fatal and can be cured with treatment.
Gastrointestinal anthrax
It is caused by eating the meat of an infected animal not cooked properly. Gastrointestinal infections affect the throat to the colon. Its problems include vomiting, loss of appetite, headache, bloody diarrhea, sore throat, and difficulty in swallowing.
Inhalation anthrax
Inhalation anthrax develops when anthrax spores are inhaled. This is the most lethal form of the disease and can be fatal even under treatment. Sore throat, fever, fatigue, muscle aches, flu-like symptoms, and shortness of breath are symptoms. It also causes circulatory collapse and meningitis.
Injection anthrax
This recently discovered anthrax infection has been found to be transmitted through illegal vaccinations. Symptoms include redness and swelling at the injection site, multiple organ failure, and meningitis.
Anthrax in animals
Animals sometimes die suddenly without showing any symptoms. There will be a high fever and chills. Also, there will be blood flow through the nose, anus, ears, mouth, etc. and the animals will die within a day or two.
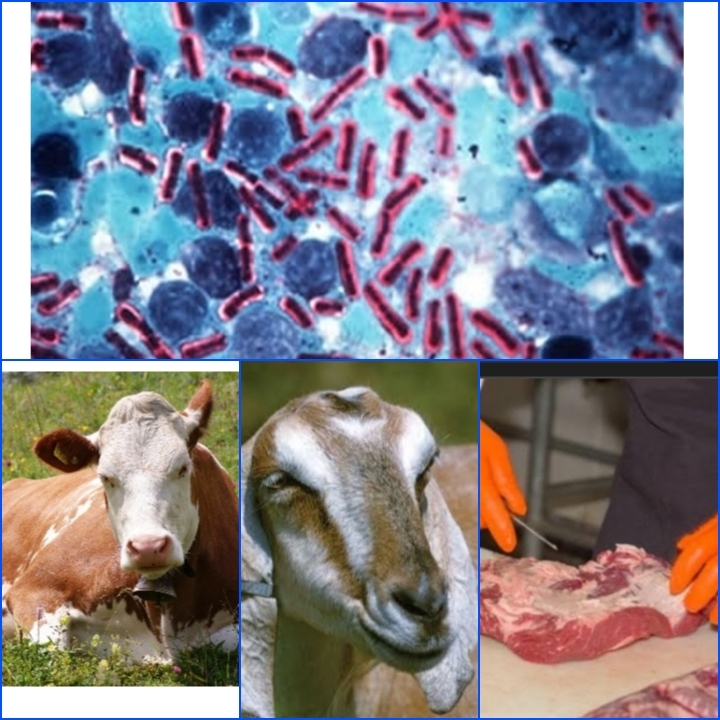
Anthrax, an animal-borne disease, is a threat to humans and cattle alike
Precautions for Anthrax (animal-borne disease) Prevention
- Cook the meat well.
- Leather industry workers should be more cautious.
- Extreme care should be taken when handling animal hides, fur, or wool from anthrax-infected areas.
- Care should also be taken when dealing with cattle.
- Care must be taken when handling and processing imported hides and wool.
- Dead animals should be handled with care.
- The carcass of infected dead animals should be dug deep and scientifically buried with lime along with the carcass or burn it.
- Vaccinate animals.
- Those who suspect that they are infected should immediately seek the advice of a doctor.
- Blood tests can be used to diagnose the disease in animals.
- Inform the local authorities immediately if an anthrax outbreak is confirmed.
- There are a few things that farmers should be aware of.
- If one of the herds gets sick, don’t replace it, replace the others.
- Do not drag the diseased dead animal away, burn it there.
- Burn all the remains like the rope that tied it, the remaining feed, dung, etc.
- The stable, surroundings and equipment should be disinfected.
- Administer anthrax spore vaccine when anthrax is transmitted.
- Antibiotics such as penicillin are effective initially.
- Strong awareness and hygiene are imperative.
Monkeypox- new animal-borne disease
Animal-borne diseases from the forest to the countryside are a matter of discussion. Monkeypox is a new disease in health news. This disease is new to us and therefore there is a lot of doubt and concern among the public and the media. However, one thing can be comforted because Monkeypox is not a fast-spreading epidemic like Covid-19. This disease is transmitted through respiratory secretions or due to close contact or when there is direct contact with the secretions of the patient’s body, as well as the clothes used by the patient, and during sexual intercourse. In short, this is not a fast-spreading disease.
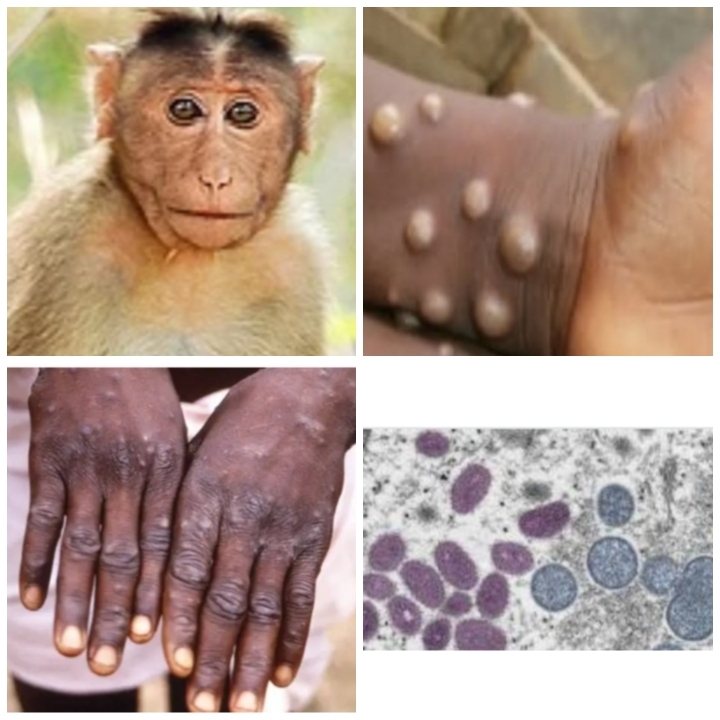
Monkeypox -some facts
- Monkeypox is a disease caused by a virus belonging to the Orthopox family.
- This disease is found in many parts of Africa.
- The name Monkeypox comes from the fact that it was first discovered in monkeys.
- But this disease is not mainly spread by monkeys.
- Small animals like rats and squirrels are the main carriers of the disease.
- Transmission of disease from these organisms to other animals in the forest is common.
- The disease can enter the human body by handling the bodies of live or dead animals.
- The disease caused by this virus in the human body is self-limited, that is, it will heal on its own.
- Those suffering from the disease should take care to drink water properly.
- Also, care should be taken to avoid other infections.
- Medications are available to reduce the severity of symptoms.
- The disease lasts from two to four weeks and is rarely serious.
- To be precise, it becomes serious only in one percent to ten percent of people.
- But we have to be careful about monkeypox.
Apart from Africa, monkeypox has been confirmed in various other countries but the death rate is low. Apart from fever and severe headache, similar to common viral fever, the main symptom is blisters that appear on the body for two to four days. Blisters are Similar to chickenpox but these blisters are thicker. Symptoms appear within four weeks of infection. The disease is likely to transmit from the day before the blisters appear. The secretions from bursting bubbles and particles released by breathing can transmit the disease. Even though it is said that the disease will heal itself, all prevention should be ensured. Eat nutritious food and drinks and take medication as per the symptoms. Treatment should be done without contact with anyone else. There is no specific medicine against monkeypox, but in cases of severe cases, medicines are given in emergency situations. There is no vaccine against monkeypox, but studies show that previous vaccination against chickenpox can protect against monkeypox to some extent. Since children do not receive this vaccine, their immunity is low, but there is nothing to worry about because the prevalence rate is low.
There is no need to worry or panic because of new disease has been confirmed. But be careful and be aware of the disease. We have managed to prevent even the fast-spreading Covid as much as possible. So, we don’t have to worry much about monkeypox.
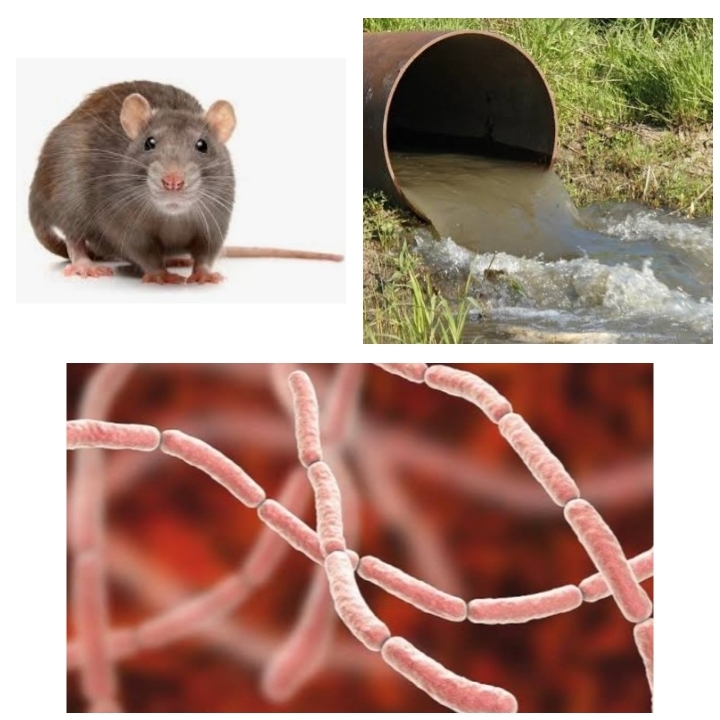

Rat fever- requires a lot of care
Rat fever is another animal-borne disease to watch out for. When animal-borne diseases become epidemics, it is a very dangerous situation. Although any age group can be infected with rat fever at any time, the risk is higher in areas with high rat infestation and waterlogged areas. Those who work in water bodies, ponds, and farms should be extra cautious. Those who work in the fields are more susceptible to the disease. Those who work in areas contaminated by rat urine need to be very careful. The pathogen enters the human body through contact with animal urine or water contaminated with animal urine. Germs can enter the body through scratches, wounds, eyes, and mouth. Infection can also occur through drinking water. The main carriers are rats, rodents, and wild animals. Organisms that harbor pathogens in the kidneys are silent carriers of pathogens. They can shed pathogens in their urine for months without showing symptoms.
Rat fever is a zoonotic disease that requires a lot of care. Rodent control methods should be used. The disease can be transmitted to humans and domestic animals through direct or indirect contact with them. The survival of bacteria excreted in urine depends on the temperature of the environment.
- Do not ignore symptoms in animals.
- Cows and buffaloes can have a high fever.
- There will also be swelling of the udder.
- Sometimes red milk coming from swollen udders is also a symptom of this disease.
- Another symptom is not taking food.
- Goats can also have these symptoms.
- It will also show signs of jaundice.
- Symptoms also include late-stage miscarriage and placental abruption in goats.
- In dogs, symptoms may be present with or without jaundice.
Precautions for prevention and control of rat fever
- First of all, rodent extermination methods should be used.
- Dogs should be vaccinated.
- Care should be taken not to mix the urine of infected rodents with feed and drinking water
- Rodent attractants should not be placed near food items
- Care should be taken to prevent rats from entering the store rooms
- The stable and its surroundings should be kept clean.
- Care should be taken when letting cattle graze in standing water and grass areas.
- Cattle should be kept away from wild animals.
- Cattle with leg or body wounds should not be bathed in contaminated water.
- Dairy farmers must wear socks and gloves while working in the fields and lands.
- If there are wounds on the limbs, they should be treated in time.
- Stagnation of wastewater should be avoided.
- After handling the animal, the limbs should be washed with soap and clean water.
- People with leg or body wounds should be careful not to step into waterlogged areas.
- Drink only boiled water.
- Personal hygiene and environmental cleanliness should be maintained.
Rabies infection- a viral disease
Rabies infection is one of the things that often comes up in health articles and causes a lot of pain in our minds. Typically, rabies is transmitted through the bite of a rabid animal. Infected animals’ saliva spreads rabies to people. Fever, headaches, excessive salivation, muscle spasms, paralysis, and confusion are some symptoms of rabies. It is now known that the virus that causes rabies belongs to the Lyssavirus genus. The rabies virus attacks the brain and spinal cord. A failure to prevent it will result in death.
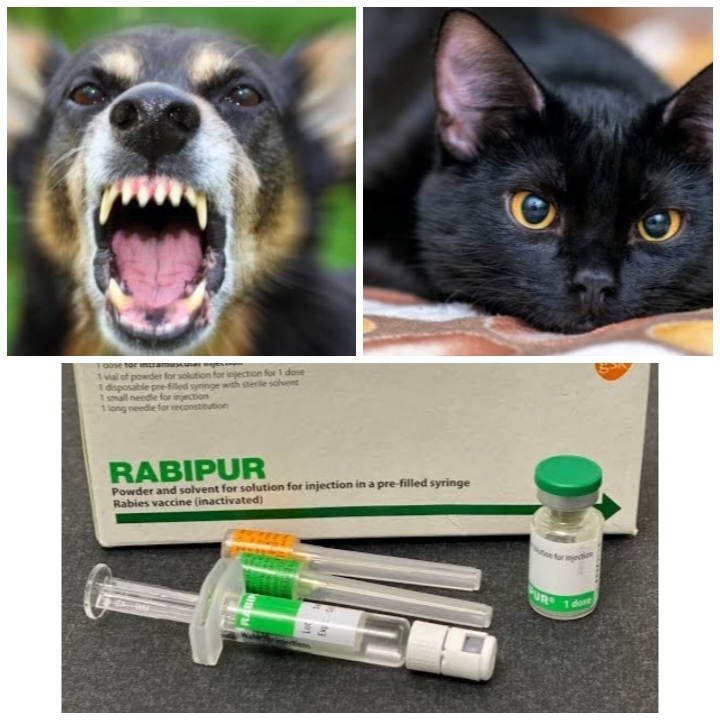
Everything you need to know about rabies infection
- Rabies is a viral disease.
- It is usually transmitted through the bite of an infected animal, usually a dog.
- Rabies is common in areas where stray dogs abound.
- A dog or cat bite should be treated immediately.
- Dog breeders should be responsible owners.
- Vaccinate dogs.
- The warnings of the authorities must be followed.
- Ninety percent of rabies is transmitted by dog bites in our country.
- There are also cat bites.
- Considering the number of rabies cases in hospitals most of those who seek treatment are bitten by their own pets.
- Once rabies infection is confirmed, there is no effective treatment.
- So, for treatment to be successful, it must be treated before symptoms appear.
- Only very few people survive rabies infection because the disease is usually fatal.
- Rabies can cause neurological problems.
- It is also common for people with rabies to feel nervous and scared when they see water.
- Early symptoms of rabies include weakness or restlessness, fever, or headache.
- There may be discomfort and itching at the site of the bite.
- Symptoms then progress to brain damage, anxiety, confusion, and agitation
There is no doubt that there have been many changes in the field of rabies prevention. It is of some relief that the painful injection around the navel has been replaced by the modern tissue culture vaccine, which can be done painlessly under the skin.
Nowadays the consumption of meat is increasing day by day. But the fact is that the means of preventing diseases that can be transmitted to humans through meat are not strong enough. Strengthening meat inspection, stopping illegal slaughterhouses, modernizing slaughterhouses, and ensuring the quality of meat are the ways to prevent the disease.
Can animal-borne diseases destroy mankind?
If you ask why animal-borne diseases come from the forest to the country and why animal-borne diseases have been rampant in the recent past, the answer is the cruelty of humans to animals and nature. The main reason is the encroachment of human beings into the natural habitats of the species. Therefore, new zoonotic diseases also came to humans from animals. Monkey fever, monkeypox, Nipa, dengue fever, rat fever, and bird flu are all familiar to us now.
All of these point to the need for a connection between man, animals, birds, and climate. The post-Covid-19 world is also discussing the concept of one world and one health. It is based on the interrelationship between nature, man, and animals. The forward journey of one world one health is achieved by balancing these three. When animal-borne diseases threaten mankind, we have to take utmost care in these three and also in prevention.
We don’t know when these epidemics will leave us, or will they become a permanent part of our lives? Don’t know either. Despite all the advances in science, what can we learn from viruses and bacteria that cannot be seen with the naked eye and are disrupting our lives? Any disturbance in the ecological balance and health of the species will have to pay a heavy price. Such an imbalance can lead to the transmission of serious infectious diseases from animals to humans and threaten the socio-cultural and economic stability of mankind. This is a reminder.
Reference: Wikipedia
Image Credit: Google
Also read:



Good write-up, I am regular visitor of one’s site, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.